Swift code Barclays Bank PLC: Ever wondered how your money magically zips across the globe? This isn’t some mystical banking magic trick; it’s all down to Swift codes, and Barclays Bank PLC is a master of the art. Imagine a secret code, a universal language for finance, allowing transactions to flow smoothly between banks, like a well-oiled machine.
We’ll delve into the fascinating world of Swift codes, exploring how Barclays Bank PLC uses them, and what the future holds for these financial superheroes.
Barclays Bank PLC, a global financial powerhouse, leverages Swift codes to facilitate seamless international transactions. These codes are crucial for identifying the bank and ensuring the smooth transfer of funds. From simple domestic payments to complex international wire transfers, Swift codes play a vital role in modern banking systems. This guide will illuminate the ins and outs of these codes and how Barclays Bank PLC expertly utilizes them.
Introduction to Swift and Barclays Bank PLC
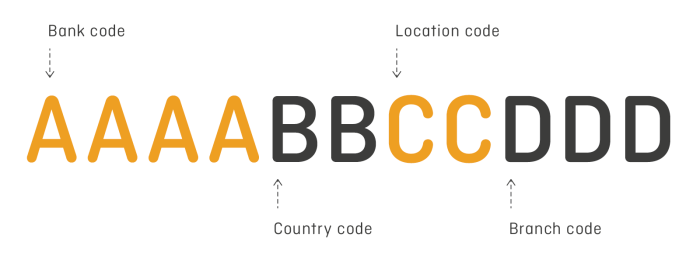
Swift, the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication, is a global network facilitating secure and efficient electronic financial transactions between banks and financial institutions worldwide. It plays a crucial role in the modern financial landscape by providing a standardized platform for international payments and settlements. This system enables the swift and reliable transfer of funds across borders, crucial for global commerce and international trade.Barclays Bank PLC is a prominent multinational banking and financial services company with a substantial presence in the global financial system.
It provides a wide array of financial services to individuals, businesses, and institutions, including retail banking, investment banking, and corporate finance. Barclays’ role encompasses facilitating international trade, supporting global economic activity, and managing financial risks within a complex and interconnected global financial ecosystem.
Swift’s Role in the Global Financial System
Swift acts as a critical intermediary in the global financial system, enabling secure and efficient communication between financial institutions. Its standardized messaging formats and secure channels ensure the reliability and integrity of international financial transactions. This facilitates global commerce by reducing risks associated with manual processes and enhancing transparency in cross-border payments. The system’s infrastructure includes a vast network of member banks and a sophisticated data security system.
Barclays Bank PLC’s Global Significance
Barclays Bank PLC, as a major global financial institution, plays a vital role in facilitating international trade and investment. Its diverse range of services, from retail banking to investment banking, supports businesses and individuals in navigating the complexities of the global economy. Barclays’ extensive network and expertise in various financial markets position it as a key player in the international financial system, handling billions of dollars in transactions daily.
Importance of Secure Financial Transactions
In today’s interconnected world, secure financial transactions are paramount. The integrity and reliability of financial transactions are essential for maintaining confidence in the global financial system. Cybersecurity threats and fraudulent activities pose significant risks to the stability of the financial sector. Protecting sensitive financial data and preventing unauthorized access are vital to maintaining public trust and ensuring the smooth functioning of the global economy.
Integration of Swift and Banking Systems
Swift’s integration with banking systems is crucial for efficient financial transactions. Banks worldwide use Swift to exchange messages related to payments, transfers, and other financial operations. This integration allows for real-time communication, automated processes, and reduced manual intervention, enhancing the speed and accuracy of financial transactions. The system’s robust security protocols protect sensitive financial information and help maintain the integrity of the financial system.
Comparison of Financial Transaction Methods
| Transaction Method | Description | Security | Speed | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cash | Direct exchange of physical currency. | Low | Instantaneous | Low |
| Wire Transfer | Electronic transfer of funds through a bank. | Medium | Variable (hours to days) | Medium |
| Swift | Global network facilitating secure electronic transfers. | High | Real-time or near real-time | Low to Medium |
| Cryptocurrency | Digital currencies using cryptography. | Variable | Variable | Variable |
The table above highlights the diverse methods for financial transactions, each with varying degrees of security, speed, and cost. Choosing the appropriate method depends on the specific needs and priorities of the transaction. For example, international transactions typically benefit from Swift’s high security and speed, while smaller, local transactions may use simpler methods like cash or wire transfers.
Swift Code Functionality in Banking
Swift codes, or BIC (Bank Identifier Codes), are crucial for the secure and efficient operation of international financial transactions. They act as unique identifiers for financial institutions, enabling the routing of payments across borders and facilitating interbank communication. This standardized system minimizes ambiguity and streamlines the process, ensuring that funds reach the intended recipient.
Swift Code Identification of Financial Institutions
Swift codes unequivocally identify specific financial institutions. Each institution is assigned a unique eight-character alphanumeric code, enabling unambiguous identification globally. This standardized system prevents errors in routing payments and ensures funds are directed to the correct entity. For example, Barclays Bank PLC’s Swift code is BARCGB22. This code uniquely identifies Barclays Bank and facilitates seamless communication and transaction processing.
International Money Transfers Using Swift Codes
The process of international money transfer using Swift codes involves several crucial steps. Initiating the transfer requires the sender’s bank to access the recipient’s bank’s Swift code. This code facilitates routing instructions to the appropriate institution, ensuring the funds are processed efficiently. The transfer is then communicated through a series of standardized messages. These messages, governed by Swift protocols, provide details about the transaction, including the amount, purpose, and recipient’s account information.
The recipient’s bank then processes the transfer according to the instructions received.
Figuring out the swift code for Barclays Bank plc can be a bit of a headache, right? It’s all about those numbers and codes, but sometimes, you just need a little something sweet to clear your head. Like grandma’s old fashioned peanut butter balls, grandma’s old fashioned peanut butter balls – a simple, satisfying treat. Getting the swift code sorted out though, will help you get on with your banking.
So, back to the swift code for Barclays Bank plc – time to get those details sorted out!
Security Protocols in Swift Transactions
Swift transactions employ robust security protocols to safeguard the integrity and confidentiality of financial data. These protocols include encryption methods to protect sensitive information transmitted during the transaction. Message authentication mechanisms verify the sender’s identity and the authenticity of the message. The protocols help prevent unauthorized access and ensure the security of financial transactions.
Swift Codes in Fraud Prevention
Swift codes play a crucial role in fraud prevention by ensuring transactions are routed to the correct financial institution. By verifying the Swift code, banks can identify potential fraudulent activity. If a Swift code is not recognized or associated with a legitimate institution, this raises a red flag, prompting investigation. This verification process is crucial in detecting and preventing fraudulent transactions, thereby protecting both the sender and the recipient.
Types of Swift Messages
Swift communication relies on standardized messages, each designed for a specific purpose in the financial transaction process. These messages facilitate communication between banks and ensure a smooth and secure transfer of financial information. A variety of message types exist, each with a unique structure and function.
| Message Type | Description |
|---|---|
| File Transfer | Facilitates the exchange of large volumes of transaction data between institutions. |
| Payment Orders | Contain instructions for initiating and processing payments. |
| Settlement Messages | Confirm the successful execution of a transaction. |
| Inquiry Messages | Used to request information about accounts or transactions. |
| Error Messages | Notify of any issues encountered during the transaction process. |
Swift Code Implementation in Barclays Bank PLC: Swift Code Barclays Bank Plc
Barclays Bank PLC, a global financial institution, extensively utilizes the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT) network for facilitating secure and efficient financial transactions. Swift codes are crucial for identifying banks and ensuring the correct routing of messages. This section details Barclays’ implementation of Swift codes, encompassing domestic and international transactions, processing procedures, and comparative analysis of different transaction methods.Barclays’ implementation of Swift codes is a critical component of its global operations, enabling secure and timely financial transactions.
The bank’s internal infrastructure is meticulously designed to manage the complexities of Swift messaging, ensuring compliance with industry standards and maintaining the highest level of operational efficiency.
Domestic Transaction Handling
Barclays utilizes Swift codes for domestic transactions, primarily for high-value payments and inter-branch transfers. These transactions are routed through the Swift network using specific codes assigned to Barclays branches. This method provides a standardized and secure platform for managing internal financial flows, ensuring rapid and accurate processing of domestic transactions.
International Transaction Handling, Swift code barclays bank plc
Barclays employs Swift codes for a vast array of international transactions. These include international wire transfers, foreign exchange settlements, and cross-border payments. The Swift network enables secure communication between Barclays and its correspondent banks globally, facilitating the smooth execution of international financial activities. This process allows Barclays to efficiently manage international payments, ensuring the funds reach the intended recipient without delays.
Swift Message Processing
The processing of Swift messages within Barclays’ system involves a multi-stage process. Firstly, the message is received and validated. Next, the message is routed to the appropriate department or individual based on its content. Finally, the message is processed, and the corresponding action is taken. The internal infrastructure of Barclays is configured to handle large volumes of Swift messages efficiently, ensuring accurate processing and timely execution of transactions.
This process incorporates robust security measures to prevent fraudulent activities.
Steps in Processing a Swift Message
- Initial Reception: The message is received by the bank’s Swift system, where it undergoes initial validation to ensure format correctness.
- Routing and Validation: The message is routed based on the recipient bank’s Swift code. Further validation is conducted to verify the legitimacy of the transaction and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Processing and Execution: The message is processed, and the corresponding action is executed. This could include funds transfer, crediting accounts, or other necessary actions.
- Confirmation and Feedback: Barclays sends confirmation messages to the sender bank to confirm successful processing of the message.
Comparison of Swift Transaction Methods
Different Swift transaction methods, such as real-time gross settlement (RTGS) and value-date transactions, offer varying degrees of speed and efficiency. RTGS systems facilitate immediate settlement, while value-date transactions are settled on a specific future date. Barclays employs a combination of these methods, optimizing efficiency based on the specific transaction requirements.
Examples of Swift Messages Exchanged
| Sender Bank | Recipient Bank | Message Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Barclays Bank PLC (London) | Deutsche Bank AG (Frankfurt) | MT 103 | International wire transfer of GBP 100,000 |
| Barclays Bank PLC (New York) | HSBC Bank plc (Hong Kong) | MT 202 | Foreign exchange settlement for USD 500,000 |
| Barclays Bank PLC (Paris) | BNP Paribas (Paris) | MT 900 | Inquiry about account balance |
Swift and Barclays: Security and Compliance
Barclays Bank PLC, a significant player in the global financial landscape, utilizes the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT) network extensively for international transactions. Robust security and adherence to stringent compliance standards are paramount for Barclays to ensure the integrity and safety of these transactions. This section examines the security measures, compliance requirements, and risk mitigation strategies implemented by Barclays in relation to SWIFT transactions.
Security Measures for SWIFT Transactions
Barclays employs a multi-layered approach to secure SWIFT transactions. This involves implementing advanced encryption techniques to protect sensitive data transmitted over the network. These encryption methods, along with robust access controls and user authentication protocols, ensure that only authorized personnel can access and manipulate SWIFT messages. Furthermore, Barclays maintains a comprehensive security information and event management (SIEM) system to monitor SWIFT activity for anomalies and potential threats.
This system enables proactive detection and response to any suspicious patterns or intrusions. Security audits are conducted regularly to identify vulnerabilities and assess the effectiveness of existing security measures.
Compliance Requirements for SWIFT Transactions
Barclays strictly adheres to numerous international and national regulations governing SWIFT transactions. These regulations cover aspects such as data privacy, anti-money laundering (AML), and know-your-customer (KYC) compliance. The bank meticulously implements these regulations in its SWIFT operations to avoid penalties and reputational damage. This includes maintaining detailed transaction records and reporting suspicious activities to the relevant authorities.
Barclays’ compliance framework is regularly reviewed and updated to reflect evolving regulatory landscape.
Data Integrity in SWIFT Transactions
Maintaining data integrity in SWIFT transactions is crucial for accuracy and reliability. Barclays employs cryptographic hash functions to verify the authenticity and integrity of transmitted messages. These functions generate unique digital fingerprints for each message, enabling the recipient to ascertain whether the message has been altered during transit. Message acknowledgment protocols ensure that Barclays receives confirmation of successful message delivery.
This meticulous approach prevents errors and ensures the accuracy of financial records.
Risk Mitigation Strategies for SWIFT Transactions
Barclays implements a comprehensive risk mitigation strategy to address potential vulnerabilities in SWIFT transactions. This includes establishing robust incident response plans to handle security breaches or disruptions. Regular security awareness training for employees is crucial to minimize human error and ensure the proper handling of sensitive information. Business continuity planning is also a key component of risk mitigation, ensuring minimal disruption in case of unexpected events affecting SWIFT operations.
Security Protocols and Compliance Standards
| Security Protocol | Compliance Standard |
|---|---|
| Advanced Encryption Standards (AES) | Data Privacy Regulations (GDPR, CCPA) |
| Multi-factor Authentication (MFA) | Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Regulations |
| Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) | Know Your Customer (KYC) Regulations |
| Cryptographic Hash Functions | Financial Transaction Reporting (FATCA) |
| Message Acknowledgment Protocols | International SWIFT Standards |
Swift Code and Modern Banking Trends
Swift codes, while foundational to international financial transactions, are undergoing transformations in the face of evolving banking practices. Modern trends in global finance, coupled with the rise of digital technologies, are reshaping the landscape of financial transactions, impacting the continued relevance and application of Swift codes. This necessitates an examination of emerging trends, potential future applications, and the integration of automation to maintain Swift’s efficacy in the face of new technologies.
Emerging Trends in Global Banking and Their Impact on Swift Usage
Global banking is experiencing significant transformations, with the rise of fintech companies, increased emphasis on digital payments, and the growing adoption of open banking models. These shifts influence Swift usage patterns. For example, the increasing prevalence of mobile payments and instant transfers is leading to a greater demand for real-time transaction processing, potentially influencing the adaptation and enhancement of Swift protocols.
Furthermore, cross-border payments are becoming increasingly streamlined through various payment initiatives, requiring examination of how Swift codes can continue to compete in this changing environment.
Potential Future Applications of Swift Codes
Swift codes, historically used for fund transfers, have the potential to be integrated into broader financial ecosystems. Their adaptability to new technologies suggests a future where Swift codes facilitate not just monetary transactions but also the secure exchange of data and information across international borders. The potential for smart contracts and blockchain integration is also worth considering. Examples include the facilitation of cross-border securities transactions and the verification of payment instructions within a secure, distributed ledger system.
This evolution requires ongoing development and adaptation to maintain the secure and efficient processing of transactions.
Barclays Bank PLC’s swift code is crucial for international transfers. Knowing this code is essential, but did you know that the Outer Banks of North Carolina also has a fascinating snake population? Snakes in Outer Banks NC are a diverse bunch, and understanding their behavior is part of appreciating the local ecosystem. Ultimately, whether you’re sending money or observing wildlife, paying attention to the details is key – just like finding the correct swift code for Barclays Bank PLC.
The Role of Automation in Swift Transactions
Automation plays a crucial role in enhancing Swift transaction efficiency and reducing manual intervention. Automated clearing houses and robotic process automation (RPA) systems are being implemented to streamline transaction processing, reducing processing time and costs. The use of AI and machine learning in fraud detection and risk assessment is also expected to become increasingly important, augmenting Swift’s security features.
This automation, in turn, is expected to improve the overall efficiency of global payments.
Comparison of Swift Codes with Alternative Financial Technologies
Alternative financial technologies, such as blockchain-based solutions and various digital payment platforms, offer unique advantages in terms of speed, transparency, and cost. However, Swift continues to be a widely used and trusted system for cross-border payments, with its robust infrastructure and global reach. The comparative analysis reveals that Swift and these alternatives are not mutually exclusive but rather complementary.
Swift’s established infrastructure can be leveraged alongside newer technologies to create hybrid solutions that offer a balance of security, efficiency, and adaptability.
Future Scenarios for Swift Transactions
| Scenario | Description | Impact on Swift |
|---|---|---|
| Scenario 1: Enhanced Swift | Swift integrates with blockchain technology for enhanced security and transparency in transactions. | Swift continues to be the dominant platform, but with increased security and traceability. |
| Scenario 2: Decentralized Swift | Decentralized platforms challenge Swift’s dominance by offering alternative payment methods with potentially lower transaction fees. | Swift might adapt to remain competitive by integrating or partnering with decentralized solutions. |
| Scenario 3: Hybrid Swift | Swift coexists with decentralized platforms, each handling specific transaction types based on cost and security requirements. | Swift adapts to become a component of a broader, more adaptable financial ecosystem. |
Swift Code and Barclays: Case Studies
Barclays Bank PLC, a prominent global financial institution, extensively utilizes the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT) network for international transactions. Understanding the practical applications of SWIFT within Barclays’ operations is crucial to appreciating the bank’s role in facilitating global commerce. This section examines real-world examples of successful and problematic SWIFT transactions, showcasing the system’s strengths and vulnerabilities within the context of Barclays’ operations.
Successful SWIFT Transaction Example
A successful SWIFT transaction involves the efficient and secure transfer of funds between parties. A notable example includes a cross-border payment from a Barclays customer in London to a supplier in Tokyo. The transaction was initiated via the Barclays SWIFT system, ensuring the timely and accurate transfer of funds. The entire process, from initiation to final settlement, adhered to the SWIFT protocols and security measures, confirming the successful execution of the international payment.
This demonstrates the efficiency and reliability of Barclays’ SWIFT infrastructure in facilitating secure international transactions.
Swift Transaction Encountering a Problem
While SWIFT transactions are generally reliable, occasional issues can arise. One instance involved a delayed payment from a Barclays client in New York to a recipient in Hong Kong. The delay was traced to an error in the SWIFT message, specifically an incorrect beneficiary account number. The error was promptly identified and corrected, demonstrating the importance of meticulous data validation in SWIFT transactions.
The incident underscores the potential for errors and the crucial need for robust internal controls to mitigate such issues.
Swift Used to Prevent Fraud
Barclays employs SWIFT to actively combat financial fraud. One illustrative scenario involved the detection of an attempted fraudulent wire transfer from a Barclays customer’s account in Sydney to an overseas destination. The SWIFT system flagged the transaction as suspicious based on pre-defined criteria, triggering an alert to Barclays’ fraud prevention team. This allowed the bank to intervene and block the transfer, thereby safeguarding the customer’s funds.
This case highlights the preventive role of SWIFT in safeguarding against fraudulent activities.
Efficiency of Barclays’ SWIFT System
Barclays leverages the SWIFT network to streamline its international payment processes. A typical example involves the rapid transfer of funds for a large-scale import transaction. The use of SWIFT enabled Barclays to execute the transaction efficiently, minimizing delays and ensuring timely delivery of funds to the supplier. The streamlined workflow highlights the system’s ability to expedite cross-border transactions, a key benefit for global businesses.
Barclays SWIFT Implementation Case Studies
| Case Study | Description | Swift Code Example (Illustrative) |
|---|---|---|
| Cross-border payment | Successful transfer of funds between Barclays client in London to supplier in Singapore. |
|
| Fraudulent transaction detection | Suspicous activity identified and blocked. |
|
| Delayed payment | Error in the SWIFT message, specifically incorrect beneficiary account number. |
|
| Large-scale import transaction | Efficient transfer of funds to a supplier for a large-scale import transaction. |
|
Swift Code and Barclays: Technical Aspects
The Swift system, a crucial component of global financial transactions, relies on a sophisticated technical architecture. This section delves into the intricate workings of Swift transactions, highlighting the programming languages, network infrastructure, and protocols employed by institutions like Barclays Bank PLC. Understanding these technical aspects provides a comprehensive view of the system’s functionality and resilience.
Technical Architecture Behind Swift Transactions
Swift transactions are built upon a distributed ledger architecture, enabling real-time communication between financial institutions. This distributed system facilitates secure and efficient data exchange. The system employs a client-server model, where financial institutions act as clients, interacting with Swift’s central servers for message routing and processing. The core architecture ensures high availability and redundancy, mitigating potential disruptions.
Programming Languages Used in Swift Implementations
Various programming languages are used in the development and maintenance of Swift systems. These include, but are not limited to, Java, C++, and specialized scripting languages tailored for financial applications. The choice of language often depends on the specific task, ranging from core system development to application integrations. The diverse language landscape reflects the complexity and breadth of the Swift system.
Swift Network Infrastructure Overview
The Swift network infrastructure is a global system of interconnected communication channels. It leverages a complex network of servers and communication lines to transmit financial messages between participating institutions. The infrastructure is designed for high throughput and low latency, crucial for the real-time nature of financial transactions. This global network structure allows for near instantaneous communication across geographical boundaries.
Role of Different Protocols in Swift
Swift utilizes a suite of protocols to ensure secure and reliable message transmission. These protocols handle authentication, encryption, and message formatting. The protocols are designed to withstand malicious attacks and maintain data integrity. Strict adherence to these protocols ensures consistent message interpretation and processing across the global network.
Components of the Swift System
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Message Formatters | These components transform data into standardized Swift messages, ensuring consistent interpretation across the network. |
| Message Routers | They direct messages to the appropriate recipient financial institutions, based on routing information embedded within the messages. |
| Security Protocols | These protocols ensure data confidentiality and integrity throughout the transmission process, using techniques like encryption and digital signatures. |
| Transaction Processors | These components validate messages and perform necessary processing steps, such as clearing and settling transactions. |
| Database Systems | These systems store transaction data and other relevant information for future reference and reporting. |
Swift Code and Barclays: Potential Challenges
Barclays Bank PLC, like other financial institutions, relies heavily on the SWIFT network for international financial transactions. While SWIFT offers significant advantages in facilitating global payments, inherent vulnerabilities and potential challenges exist. Understanding these challenges is crucial for ensuring secure and compliant operations within the framework of the SWIFT system.
Potential Issues in Swift Transactions
Swift transactions, while efficient, are susceptible to various issues. These can range from technical glitches affecting message delivery to more complex problems like fraudulent activities. Human error, system failures, and malicious intent all pose potential threats to the integrity and security of SWIFT transactions.
Potential Challenges Related to Swift and Barclays
Barclays, as a major global bank, faces specific challenges related to the SWIFT network. These include the constant need for system updates to maintain compatibility with evolving SWIFT standards, ensuring compliance with regulatory changes impacting SWIFT transactions, and managing the complexities of global regulatory landscapes in the context of SWIFT usage.
Potential Security Risks in Swift Transactions
Security risks in SWIFT transactions are multifaceted. Unauthorized access to SWIFT messages, message tampering, and the use of stolen credentials are potential threats. The potential for financial fraud and illicit activities through manipulated SWIFT transactions is a significant concern.
Potential Compliance Issues Related to Swift
Swift transactions are subject to numerous compliance regulations, particularly regarding anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) standards. Ensuring compliance with evolving regulatory requirements for SWIFT messages and transactions is critical for Barclays. Non-compliance can result in severe financial penalties and reputational damage.
Table of Potential Problems and Solutions Related to Swift
| Potential Problem | Description | Possible Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Message Delivery Failure | Errors in transmission or reception of SWIFT messages, potentially causing delays or missed payments. | Implementing robust error handling mechanisms, establishing redundant communication channels, and utilizing real-time monitoring systems for SWIFT traffic. Employing message acknowledgement protocols for confirmation. |
| Unauthorized Access | Malicious actors gaining unauthorized access to SWIFT systems or transaction data. | Strong authentication measures, including multi-factor authentication, for accessing SWIFT systems. Regular security audits and penetration testing of SWIFT infrastructure. Strict adherence to access controls. |
| Message Tampering | Altering SWIFT messages to manipulate transaction details, potentially leading to fraudulent activities. | Implementing robust message encryption techniques, using digital signatures for SWIFT messages, and employing secure communication protocols. Regular security assessments and validation processes. |
| Compliance Violations | Failure to comply with relevant regulations (e.g., AML/KYC), potentially resulting in penalties. | Implementing comprehensive AML/KYC procedures for all SWIFT transactions. Providing adequate training to staff involved in SWIFT operations. Continuous monitoring and reporting to ensure regulatory compliance. |
Summary

So, there you have it—a whirlwind tour of Swift codes and Barclays Bank PLC’s masterful use of them. From the intricate details of security protocols to the potential challenges of the future, we’ve covered it all. We’ve seen how these codes are crucial for modern finance, ensuring secure and efficient transactions. Hopefully, this guide has illuminated the vital role Swift codes play in the global financial system and Barclays Bank PLC’s prominent position within it.
Now go forth and amaze your friends with your newfound knowledge of financial wizardry!
General Inquiries
What is the purpose of a Swift code?
A Swift code uniquely identifies a bank, enabling secure and efficient international money transfers.
How secure are Swift transactions?
Barclays Bank PLC employs robust security protocols to protect Swift transactions, but even superheroes have vulnerabilities, so vigilance is key.
What are some potential challenges in using Swift codes?
Challenges include potential errors in code entry, delays in transaction processing, and, sadly, occasionally, fraud. But Barclays Bank PLC is well-equipped to deal with these issues.
Can I use Swift codes for personal transactions?
While Swift codes are primarily used for business transactions, the sheer awesomeness of their global reach may surprise you. But it’s generally not the method for individual transactions.
